Question 1:
(a) Diagram 1.1 shows some of the cell components involved in the production of an extracellular enzyme.

(i) Label ribosome on Diagram 1.1. [1 mark]
(ii) State the function of K. [1 mark]
(iii) Give one example of extracellular enzyme produced in Diagram 1.1. [1 mark]
(b) Diagram 1.2 shows a part of the human digestive system.
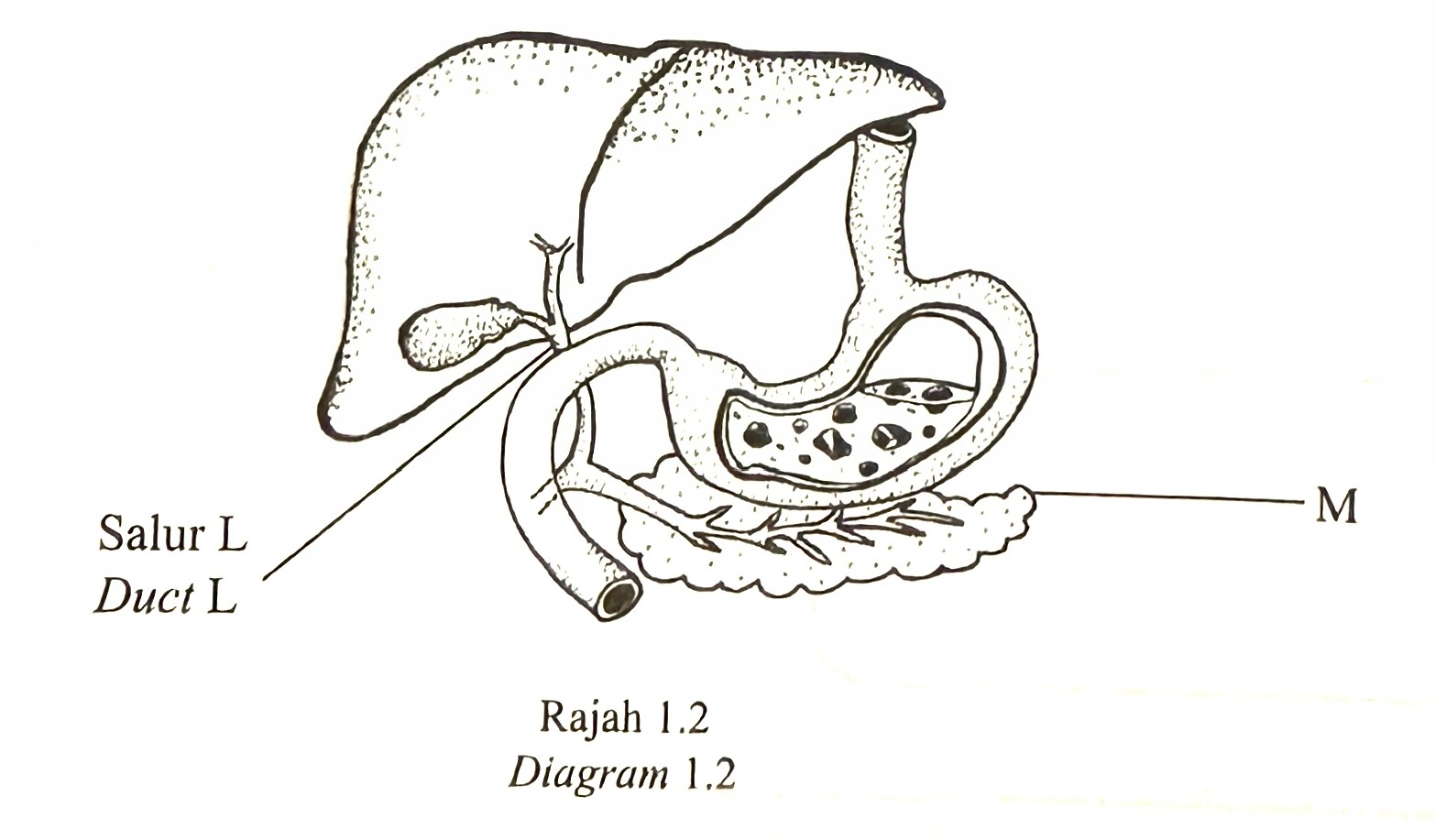 (i) State the name of organ M. [1 mark]
(i) State the name of organ M. [1 mark]
(ii) Give one characteristic of the enzyme secreted by organ M. [1 mark]
(iii) Duct L of an indvidual is blocked. State why the digestion of lipid become slower in duodenum. [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i)

(a)(ii)
P1: Processes, modifies chemicals such as proteins
P2: Packing and transporting materials chemicals such as enzymes, carbohydrates and glycoproteins
(a)(iii) Trypsin / Lipase / Any correct extracellular enzyme
(b)(i) Pancreas
(b)(ii)
P1: Enzymes are needed in small quantities.
P2: Enzymes can be reused
P3: Enzyme action is specific.
Any one answers
(b)(iii)
P1: Bile cannot be channeled (to the duodenum)
P2: pH is not optimal / not alkaline / acidic
P3: Lipids is not emulsified/(total) lipid surface area is small
P4: The hydrolysis process is reduced
Any one answers
(a) Diagram 1.1 shows some of the cell components involved in the production of an extracellular enzyme.

(i) Label ribosome on Diagram 1.1. [1 mark]
(ii) State the function of K. [1 mark]
(iii) Give one example of extracellular enzyme produced in Diagram 1.1. [1 mark]
(b) Diagram 1.2 shows a part of the human digestive system.
 (i) State the name of organ M. [1 mark]
(i) State the name of organ M. [1 mark](ii) Give one characteristic of the enzyme secreted by organ M. [1 mark]
(iii) Duct L of an indvidual is blocked. State why the digestion of lipid become slower in duodenum. [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i)

(a)(ii)
P1: Processes, modifies chemicals such as proteins
P2: Packing and transporting materials chemicals such as enzymes, carbohydrates and glycoproteins
(a)(iii) Trypsin / Lipase / Any correct extracellular enzyme
(b)(i) Pancreas
(b)(ii)
P1: Enzymes are needed in small quantities.
P2: Enzymes can be reused
P3: Enzyme action is specific.
Any one answers
(b)(iii)
P1: Bile cannot be channeled (to the duodenum)
P2: pH is not optimal / not alkaline / acidic
P3: Lipids is not emulsified/(total) lipid surface area is small
P4: The hydrolysis process is reduced
Any one answers
Question 2:
Diagram 2 shows a type of tissue on the surface of trachea.

(a) State the name of projection P. [1 mark]
(b) Tissue in Diagram 2 produces mucus.
(i) State the name of the tissue. [1 mark]
(ii) Explain the role of mucus in the first line of body defence. [2 marks]
(c) A sprinter carries out intensive training every day to increase the density of mitochondria in his muscle cells. Explain how the increase in the density of mitochondria helps the sprinter during a tournament. [2 marks]
Answer:
(a) Cilia / Cilium
(b)(i) Epithelial tissues
(b)(ii)
P1: Mucus contains lysozyme.
P2: to destroy airborne bacteria that enter the respiratory system
OR
P1: Traps bacteria/pathogens
P2: Through sticky fluid
(c)
P1: Respiration rate increases
P2: Produces a lot of energy / ATP
P3: Increased muscle contraction (and relaxation) // running fast
Any two answers
Diagram 2 shows a type of tissue on the surface of trachea.

(a) State the name of projection P. [1 mark]
(b) Tissue in Diagram 2 produces mucus.
(i) State the name of the tissue. [1 mark]
(ii) Explain the role of mucus in the first line of body defence. [2 marks]
(c) A sprinter carries out intensive training every day to increase the density of mitochondria in his muscle cells. Explain how the increase in the density of mitochondria helps the sprinter during a tournament. [2 marks]
Answer:
(a) Cilia / Cilium
(b)(i) Epithelial tissues
(b)(ii)
P1: Mucus contains lysozyme.
P2: to destroy airborne bacteria that enter the respiratory system
OR
P1: Traps bacteria/pathogens
P2: Through sticky fluid
(c)
P1: Respiration rate increases
P2: Produces a lot of energy / ATP
P3: Increased muscle contraction (and relaxation) // running fast
Any two answers