(a) Figure 2.1 shows patterns of a few thumbprints.
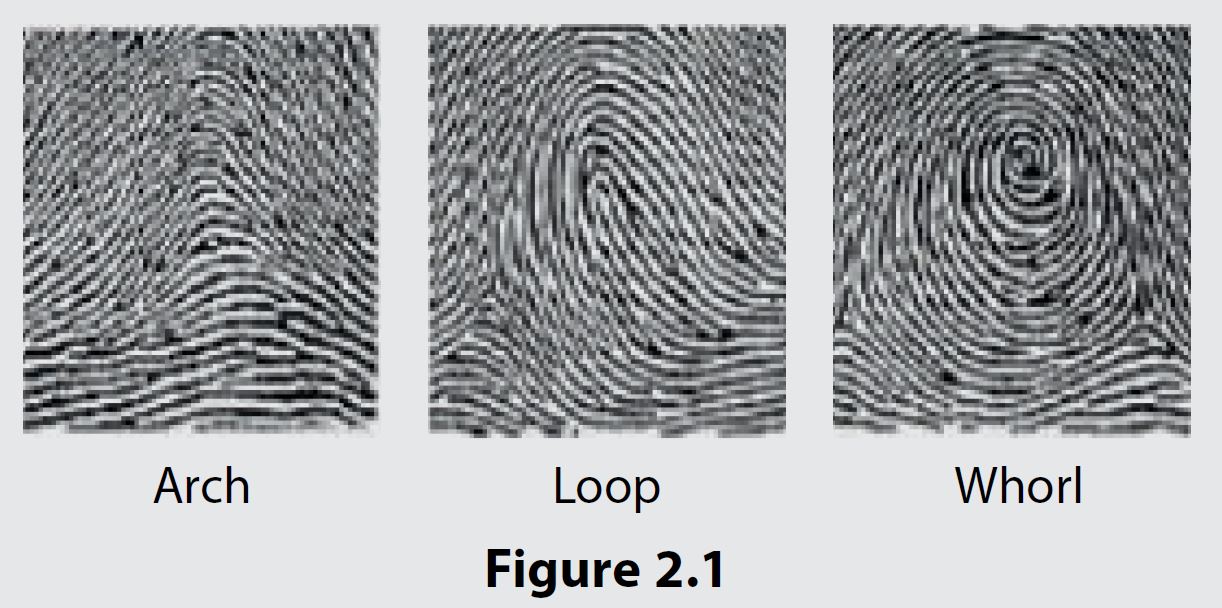

Identify the types of variations for the thumbprint pattern and discuss the factors that cause these variations.
(b)(i) State the difference between gene mutation and chromosomal mutation.
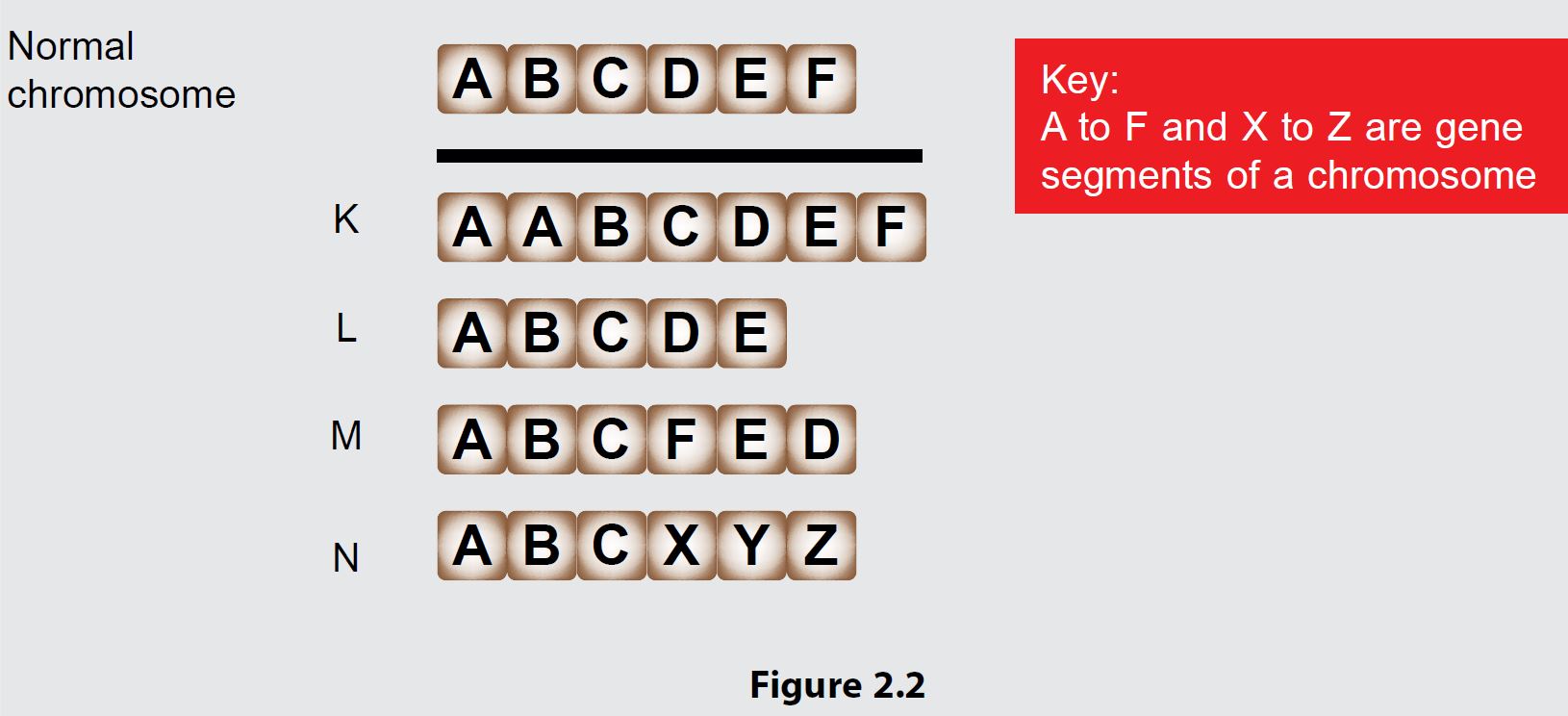
(b)(ii) Figure 2.2 shows four types of chromosomal mutations K, L, M and N. Based on Figure 2.2, explain the mutation types of K, L, M and N.
Answer:
(a)
• Thumbprint pattern is an example of discontinuous variation.
• It is influenced by genetic factor.
• During gametogenesis / gamete formation, crossing over occurs during prophase I in meiosis
• Exchange of genetic material / DNA segment occurs at sister chromotids of homologous chromosome pair.
• It produces new genetic combination in gamete.
• During metaphase I in meiosis, independent assortment of chromosome takes place.
• Homologous chromosomes are arranged randomly in equatorial plane of cell during metaphase.
• Separation of homologous pair produces gametes with different genetic combinations.
• One haploid gamete fertilises at random with another haploid gamete.
• This will produce a diploid zygote with new combination of genes.
(b)(i)
• Gene mutation involves change in nucleotide base sequence in DNA molecule of a chromosome whereas chromosomal mutation involves change in structure and number of chromosomes.
• Types of gene mutation include deletion / insertion / substitution of base in a gene whereas types of chromosomal mutation include duplication / deletion/ inversion / translocation of a chromosome segment.
(b)(ii)
• Mutations of chromosomes K, L, M and N cause change in chromosomal structures.
• K is duplication.
• Part of the chromosome in gene A undergoes duplication.
• Mutant chromosome has two sets of gene A.
• L is deletion.
• Chromosome is cut between gene E and gene F, and F is lost.
• Mutant chromosome does not have gene F.
• M is inversion.
• The segment with D, E and F genes is cut, and the same segment is rejoined but in the opposite direction.
• N is translocation.
• Cutting of the chromosome between gene C and gene D; and another chromosome segment with genes X, Y and Z joins at gene C.