Diagram shows two types of twins.
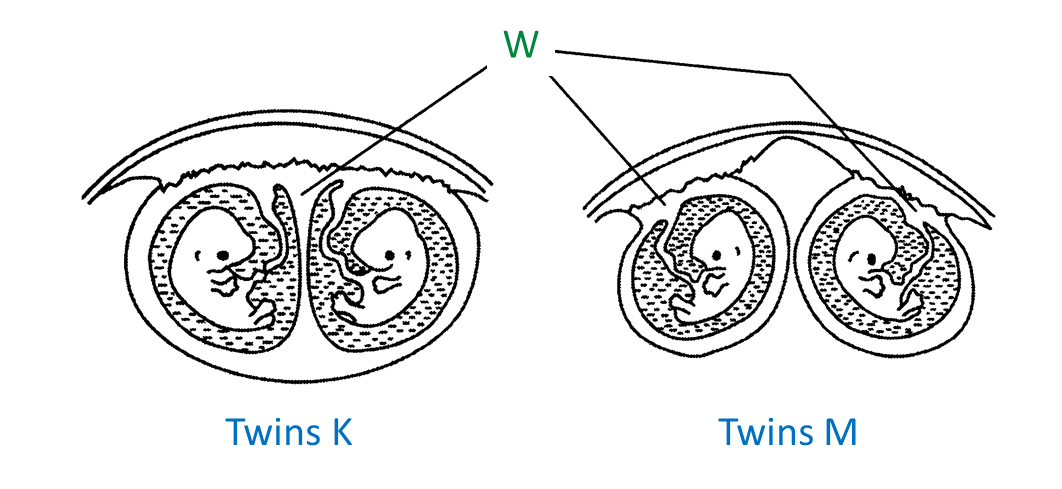
(a)(i) Name the type of twins M. [1 mark]
(ii) Explain how twins M are formed. [2 marks]
(b)(i) Name the structure W. [1 mark]
(ii) State two functions of structure W. [2 marks]
(c) State two differences between twins K and twins M. [2 marks]
(d) Twins K are brought up by two different adopted families. The twins do not have the same body size when they are adult.
Explain why. [2 marks]
(e) A woman who is a heavy smoker becomes pregnant.
Explain why she should stop smoking. [2 marks]
Solution:
(a)(i)
Fraternal twins
(a)(ii)
When two ova are released from an ovary at the same time, the ova are fertilised by two different sperms at the same time and two different zygotes are formed.
(b)(i)
Placenta
(b)(ii)
– Provides nutrients for the growth of the foetus
– Secretes oestrogen and progesterone
– Helps to remove waste/ excretory products from the foetus
(c)
- Twins K share the same placenta whereas twins M have separate placentae.
- Twins K possess identical genetic constituents whereas twins M has different genetic constituents.
- Twins K are similar in physical appearance but twins M are not.
(d)
They may have different eating habits and different daily activities.
(e)
– Chemicals such as nicotine can diffuse through the placenta to the foetus and may cause brain damage.
– Carbon monoxide can diffuse through the placenta to the foetus. This will deprive the foetal tissues for oxygen.