Figure 1 shows three examples of tissues which are found in plants.
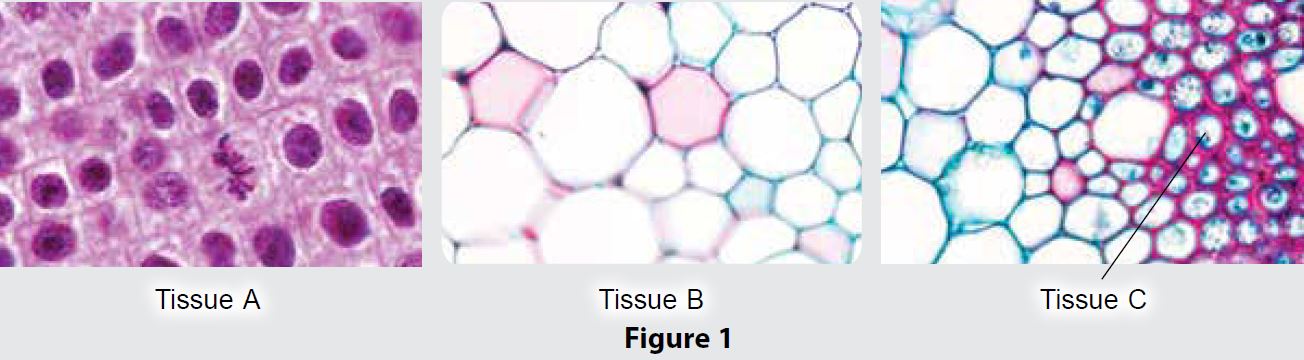
Identify tissue A, tissue B and tissue C. State one characteristic and function of each tissue.
Answer:
Tissue A: Meristematic tissue
Characteristic: Has thin cell walls, large nucleus, dense cytoplasm and small vacuoles.
Function: Young tissue that actively divides through mitosis
Tissue B: Collenchyma tissue
Characteristic: Cells walls made of pectin and hemicellulose
Function: Provides mechanical support and elasticity to plants
Tissue C: Sclerenchyma tissue
Characteristic: Has a very thick cell wall
Function: Provides support and mechanical strength to the parts of matured plants.
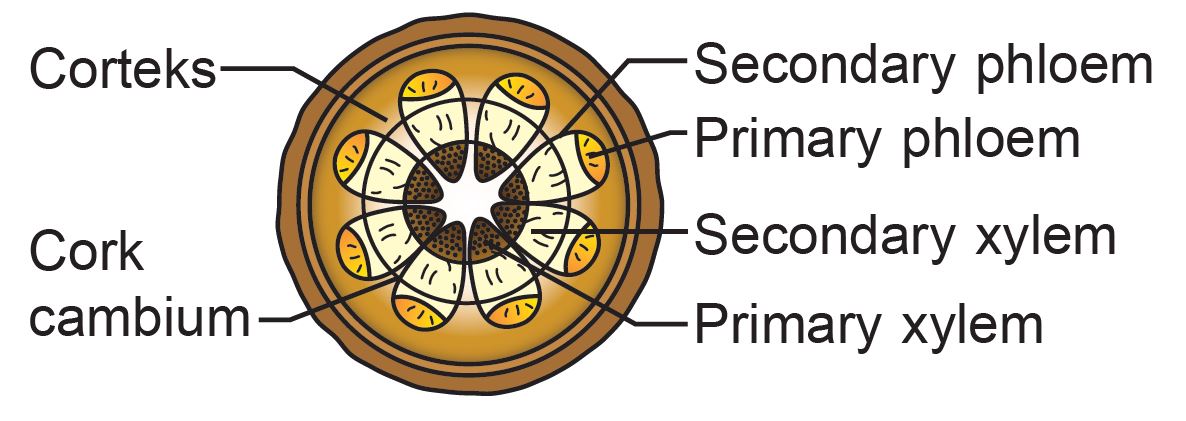
Figure 2 shows a longitudinal cross-section of a eudicot shoot tip.
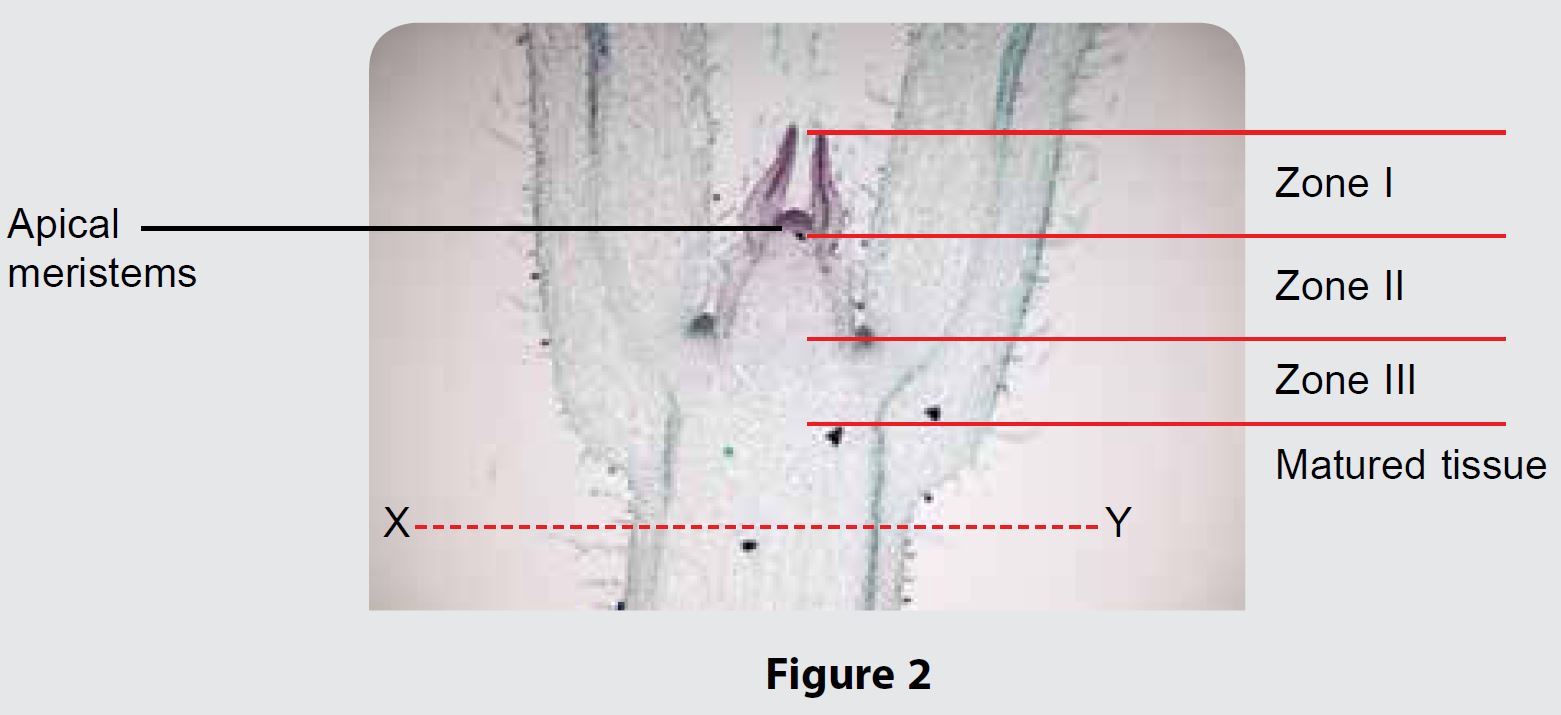

(a) Name Zone I, Zone II and Zone III.
(b)(i) Draw a cell to represent Zone I and Zone II.
(ii) State the differences between the cell in Zone I and cell in Zone II.
(c) Draw a cross-section of the shoot at XY.
(d) After a few years, the plant undergoes secondary growth. Draw a cross-section of the plant stem which has undergone the secondary growth.
Answer:
(a)
Zone I: Zone of cell division
Zone II: Zone of cell elongation
Zone III: Zone of cell differentiation
(b)(i)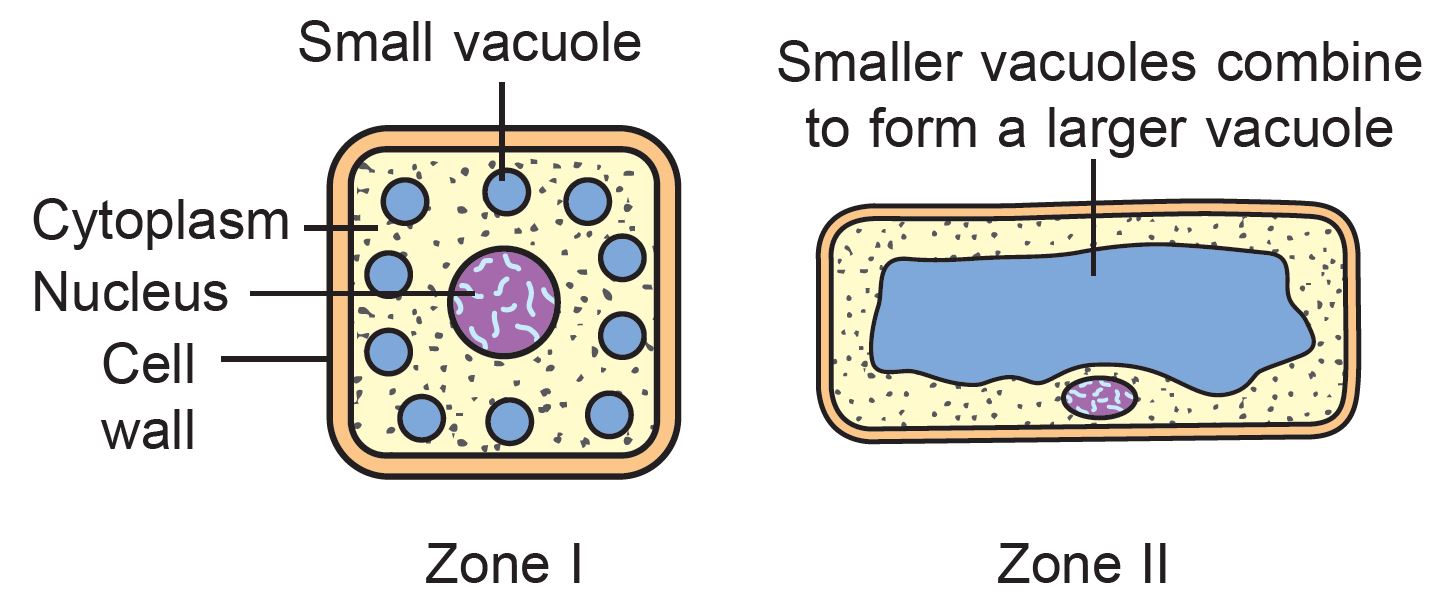
(b)(ii)
The cells in Zone I have larger nucleus compared to the nucleus found in cells from Zone II.
Most cells in Zone I have small vacuoles while cells in Zone II have large vacuoles.
(c)
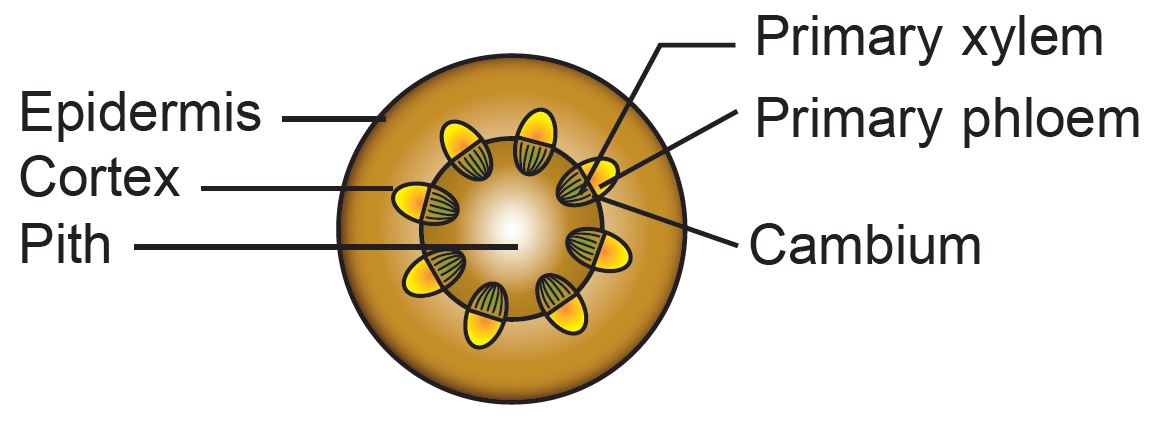
(d)