Question 1:
Diagram below shows a longitudinal section of the reproductive parts of a flower during fertilization.
(b)(i) In the space below, draw a section through the ovule, showing all the cells in M.
(b)(ii) What is the significance of having two K structures in the fertilization?
(c) In the Diagram, the structure Y has to be kept dormant for future research purposes.
(i) Explain how Y can be prevented from germinating.
(ii) If Y is to be germinated, suggest one method to stimulate the germination of Y.
Answer:
(a)
J : Pollen tube
K : Male gamete
L : Ovary
M : Embryo sac
Diagram below shows a longitudinal section of the reproductive parts of a flower during fertilization.
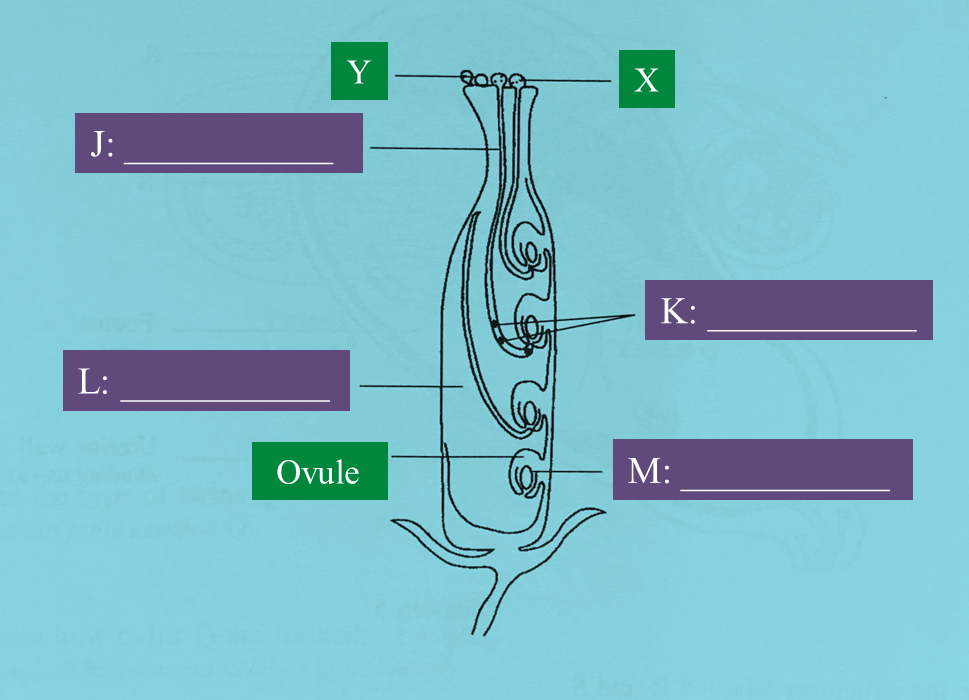
(a) On the Diagram, name the structures J, K, L and M.
(b)(i) In the space below, draw a section through the ovule, showing all the cells in M.
(b)(ii) What is the significance of having two K structures in the fertilization?
(c) In the Diagram, the structure Y has to be kept dormant for future research purposes.
(i) Explain how Y can be prevented from germinating.
(ii) If Y is to be germinated, suggest one method to stimulate the germination of Y.
Answer:
(a)
J : Pollen tube
K : Male gamete
L : Ovary
M : Embryo sac
(b)(i)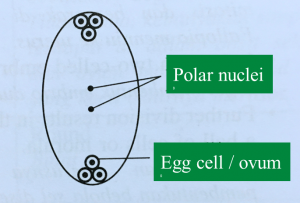
(b)(ii)
– One K/ male gamete fertilizes an egg cell to form a diploid zygote.
– One more K fuses with two polar nuclei to form a triploid zygote.
(c)(i)
– Keep Y in a dry place
– Moisture initiates germination
(c)(ii)
Spraying a sugary solution onto Y