Diagram 3 shows a human digestive system.
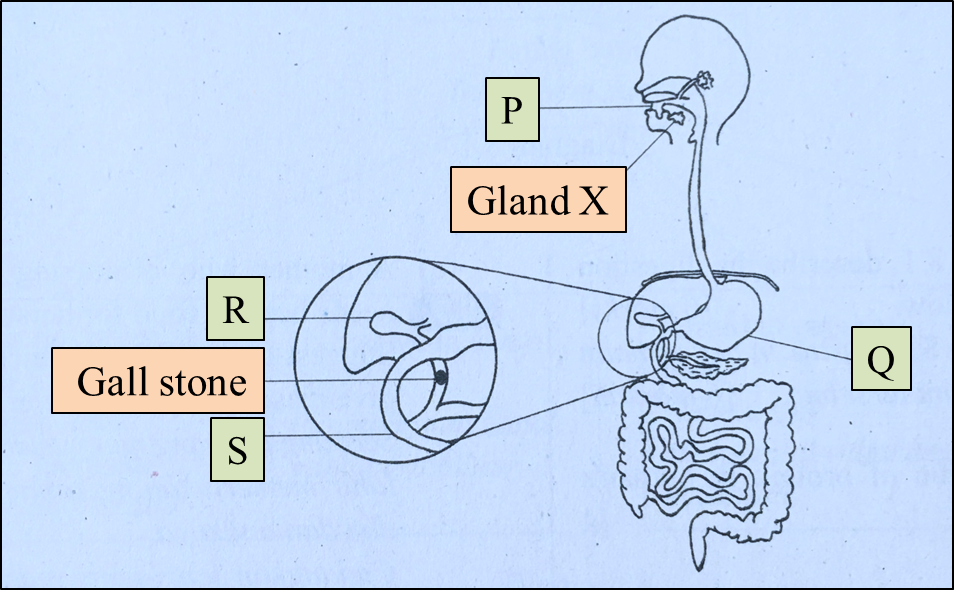 Diagram 3
Diagram 3
(a)(i) Name gland X. [1 mark]
(ii) Bread contains starch.
Explain the role of gland X in the digestion of bread in P. [3 marks]
(iii) Explain why the process of digestion of bread does not occur in Q. [3 marks]
(b)(i) Name organ R. [1 mark]
(ii) A person has a gallstone as in Diagram 3. Explain the effect of this condition to the digestion of lipid in S. [2 marks]
(c) Explain one difference in the digestion of protein that occurs in Q and S. [2 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
Salivary gland
(a)(ii)
– Gland X produces saliva
– Saliva contains the salivary amylase enzyme.
– Salivary amylase hydrolyses / digests starch into maltose.
(a)(iii)
– Q (stomach) produces gastric juice.
– Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid.
– Hydrochloric acid denatures / inhibits the action of salivary amylase. (Hence the digestion of starch in bread is stopped)
(b)(i)
Gall bladder
(b)(ii)
– Gall stone in the bile duct prevents the flow of bile from liver to duodenum.
– Bile emulsifies fat hence with the absence / lower amount of bile, the digestion of lipid is slowed down.
(c)
– In Q (stomach), protein is digested by pepsin enzyme in an acidic medium to form peptides.
– In S (duodenum), peptides are digested by trypsin enzyme in an alkaline medium to form dipeptides.
Diagram 4.1 shows the gland J and adrenal glands which secrete hormones that involve in regulating the content of water and salt in blood.
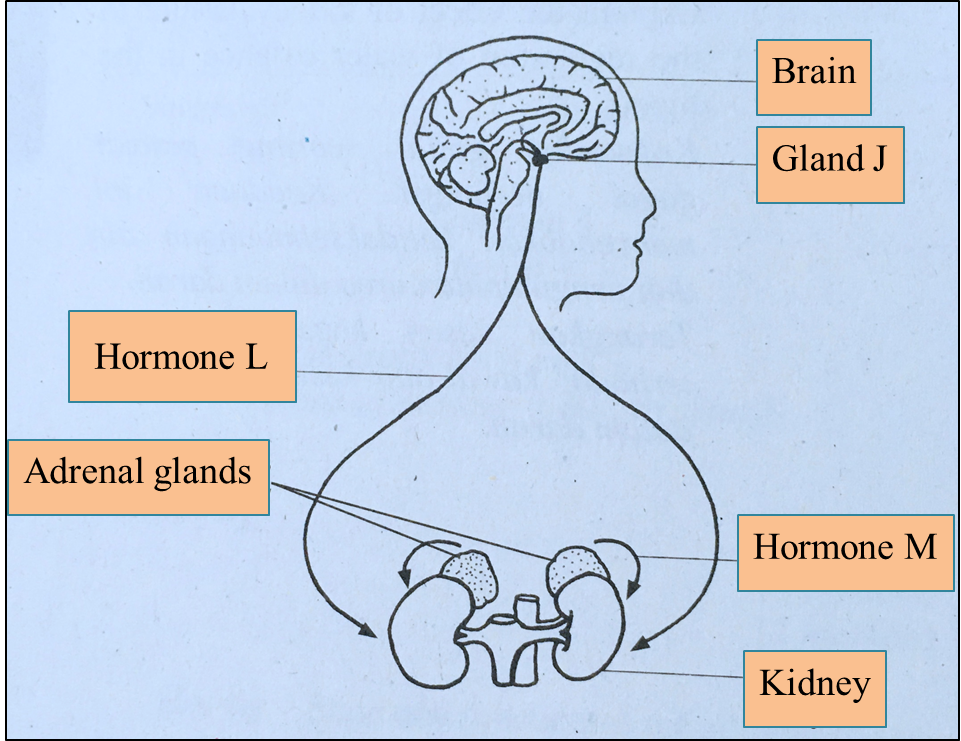 Diagram 4.1
Diagram 4.1
(a)(i) Name the hormones L and M. [2 marks]
(ii)The water content in blood is lower than the normal range.
Explain how gland J regulates the water balance in the blood. [3 marks]
(b)
Explain the action of adrenal glands to overcome the situation above in regulating the body temperature. [3 marks]
(c) Diagram 4.2 shows the process of haemodialysis.
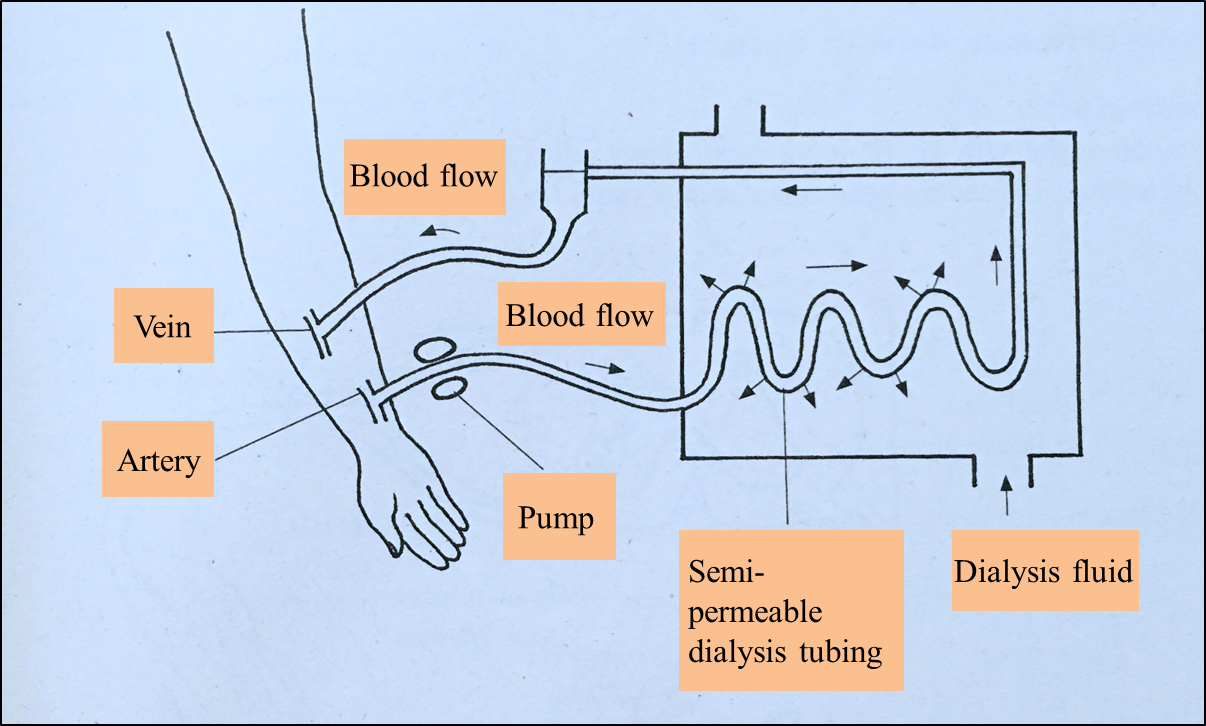 Diagram 4.2
Diagram 4.2
Explain what will happen if the semi-permeable tubing is straightened. [2 marks]
(d) The information below shows the symptoms of a patient with kidney failure.
- Swelling of leg
- Breathing difficulties due to extra fluid in lungs
- Blood in urine
Discuss the consequences of the kidney failure to the patient. [2 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
L : Antidiuretic hormone
M : Adrenaline
(a)(ii)
- Gland J (pituitary gland) secretes excessive antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
- ADH increases the permeability of the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts to water.
- More water is reabsorbed from the glomerular filtrate into blood and the osmotic pressure of blood is returned to normal level.
(b)
- The adrenal glands secrete excess adrenaline.
- Adrenaline increases the rate of conversion of glycogen into glucose.
- Adrenaline also increases the heart rate, hence more blood sugar / glucose is provided to the muscles.
- Metabolic rate increases and more heat is produced, hence the body temperature raises.
(c)
- The rate of blood dialysis will be lowered.
- Total surface area of the tubing decreases causing less blood is treated / purified per unit time.
(d)
- The swelling of legs is due to the accumulation of interstitial fluid in tissues of the legs as the fluid is not returned in blood stream.
- The accumulation of interstitial fluid in the lungs causes the rate of diffusion of respiratory gases across the alveoli to be reduced, resulting in breathing difficulties.
Since the nitrogenous waste in blood are not removed through urine, glomeruli and kidney tubules are damaged resulting in bleeding.