Diagram 1.1 shows the structure of a plant cell.
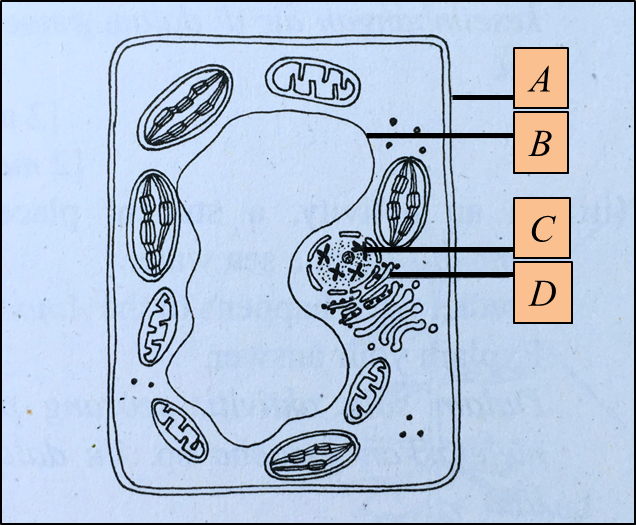 Diagram 1.1
Diagram 1.1
(a) Name the structures C and D. [2 marks]
(b)(i) State the component which forms structure C. [1 mark]
(b)(ii) Draw and label the basic unit structure of the main component which is named in 1(b)(i). [2 marks]
(c) The cell in Diagram 1.1 is immersed in distilled water for an hour.
(i) Explain what will happen to the structure B. [3 marks]
(ii) Explain why the cell does not burst. [2 marks]
(d) Diagram 1.2 shows two examples of tissues in plants.
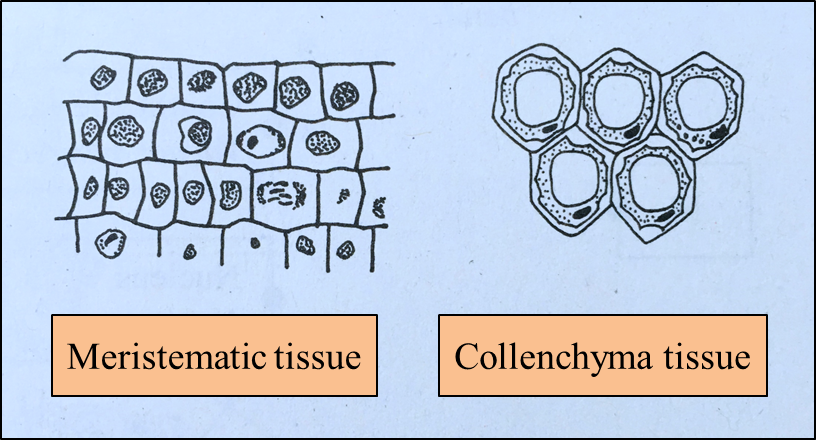 Diagram 1.2
Diagram 1.2
Based on Diagram 1.2, state a characteristic of each tissue.
(i) Meristematic tissue:
(ii) Collenchyma tissue: [2 marks]
Answer:
(a)
C : Chromosome / Chromatin
D : Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(b)(i)
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
(b)(ii)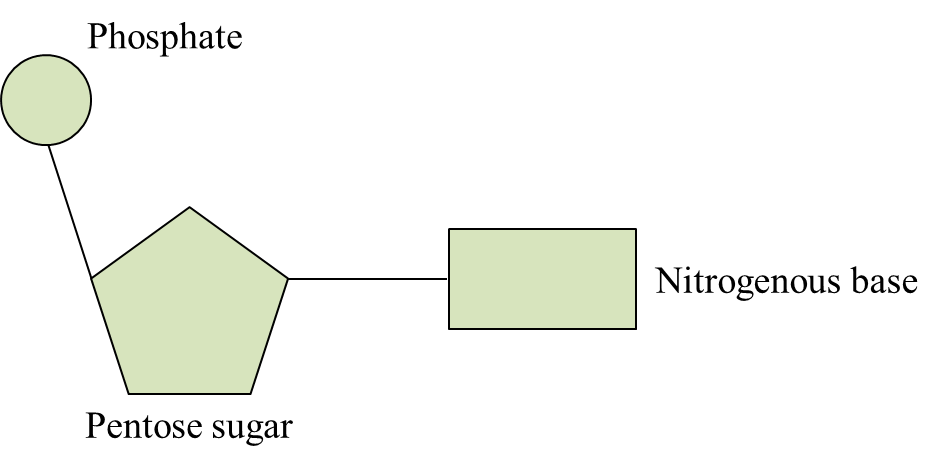
(c)(i)
Structure B (vacuole) will swell or increase in size.
– The vacuole contains cell sap which is hypertonic (to distilled water).
– Water molecules diffuse into the cell by osmosis and fill the vacuole causing it to swell.
(c)(ii)
– Plant cells are surrounded by a strong and rigid cell wall.
– Cell wall is able to withstand the strong turgor / hydrostatic pressure that develops within the cell.
(d)(i)
– Small-sized cells
– Dense cytoplasm / lack of vacuoles
– Large nucleus / nucleus at various stage of division / mitosis
– Undifferentiated cell
(Any one of the characteristics)
(d)(ii)
– Cell wall is not uniformly thickened
– Corners of cell have thicker cell wall
(Any one of the characteristics)
Diagram 2.1 shows the foods which contain carbohydrates.
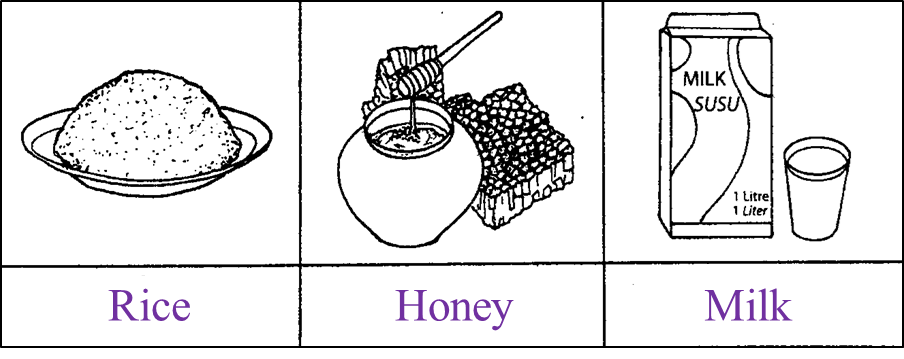 Diagram 2.1
Diagram 2.1
(a)(i) Based on diagram 2.1, name the type of carbohydrates in rice and honey. [2 marks]
(a)(ii) Explain why diabetic patients are advised not to consume excessive amount of rice in their daily diet. [3 marks]
(b) Diagram 2.2 shows the formation of molecule R in milk.
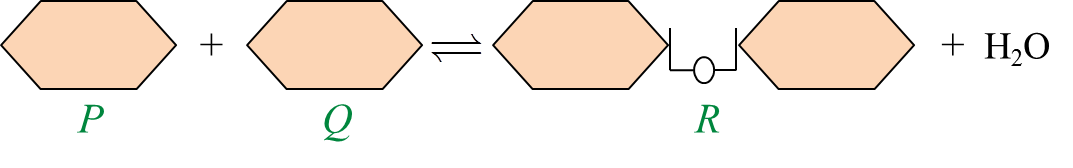 Diagram 2.2
Diagram 2.2
Based on the diagram 2.2, describe:
(i) the formation of molecule R. [2 marks]
(ii) the breakdown of molecule R. [2 marks]
(c) When sucrose solution is heated with Benedict’s solution, the blue solution remains unchanged.
Explain why Benedict’s test gives negative result on sucrose. [3 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
Rice : Starch
Honey : Fructose / glucose / sucrose
(a)(ii)
- When rice is completely digested, it produces glucose.
- Diabetic patients lack / produce lower amount of insulin hormone.
- They are unable to convert excessive glucose into glycogen, hence the higher concentration of glucose in blood.
(b)(i)
- Molecule R is disaccharide.
- It is formed when two molecules of monosaccharide are linked together by condensation reaction / with the loss of water molecule.
(b)(ii)
- Molecule R is hydrolysed / digested by the addition of a water molecule by an enzyme.
- To form its component monosaccharides / P and Q.
(c)
- Sucrose is non-reducing sugar.
- Sucrose unable to reduce the blue copper (II) ions / Cu2+ (aq) in Benedict’s solution.
- Red copper (I) ions / Cu+ (aq) are not produced / formed.