(a) Petiole and lamina are external structures of a leaf. State the function of these two structures.
(b) A leaf is a plant organ that is flat, thin and green in colour. Explain the importance of these characteristics on the function of a leaf.
Answer:
(a)
Petiole is the leaf stalk that connects lamina to the stem of the plant, lamina is the part that involved in photosynthesis.
(b)
Flat and thin to increase the surface area and maximise the exposure of leaf cells towards the Sun. The green colour is the pigment colour for chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs the red and blue light from sunlight for photosynthesis.
Other than chlorophyll pigment, plants also have carotenoids, which are yellow, orange and red pigments that can absorb light energy from the sun to carry out photosynthesis. Explain the differences of chlorophyll and carotenoids involvement in photosynthesis.
Answer:
Chlorophyll absorbs red light whereas carotenoids absorb blue light before moving to chlorophyll to excite the electron in light dependent reaction.
A group of students carry out an experiment to investigate the distribution of stomata on mint and thyme leaves. Thyme plants have less number of leaves than mint plants. Table 1 shows the results of the experiment.
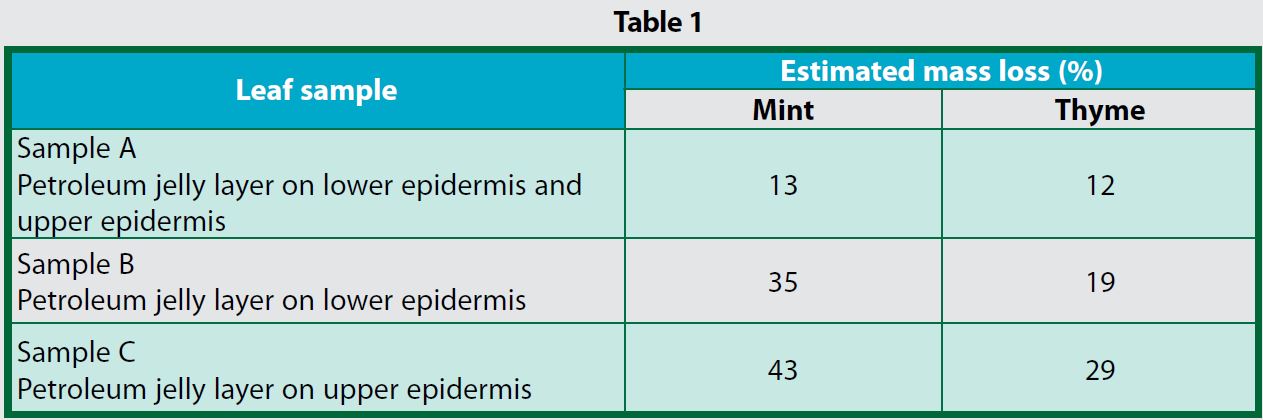
(a) For mint leaf, which sample loses water the most? Explain.
(b) For thyme leaf, which sample has the highest distribution of stoma? Explain.
(c) Explain the differences of both leaves based on the results of the experiment.
(d) Based on the results of the experiment, which plant can adapt to a hot and dry surrounding condition? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
(a)
Sample C because the lower surface of the leaf is not covered with petroleum jelly. The petroleum jelly prevents water evaporation.
(b)
Sample C because the lower surface of the leaf is not covered with petroleum jelly. Petroleum jelly prevents water evaporation through the stoma. This means the stomatal distribution is higher on the lower surface of the leaf.
(c)
| Pudina leaf | Characteristic | Thyme leaf |
| Abundant | Number of leave | Few |
| Abundant | Distribution of stoma on the upper surface of the leaf | Few |
| Abundant | Distribution of stoma on the lower surface of the leaf | Few |
| Abundant | Mass of water lost | Few |
(d)
The thyme plant because it has fewer stomata that helps to prevent excessive loss of water