Question 9:
(a) Diagram 9.1 shows a membrane lining that is involved in the human first line of defence.
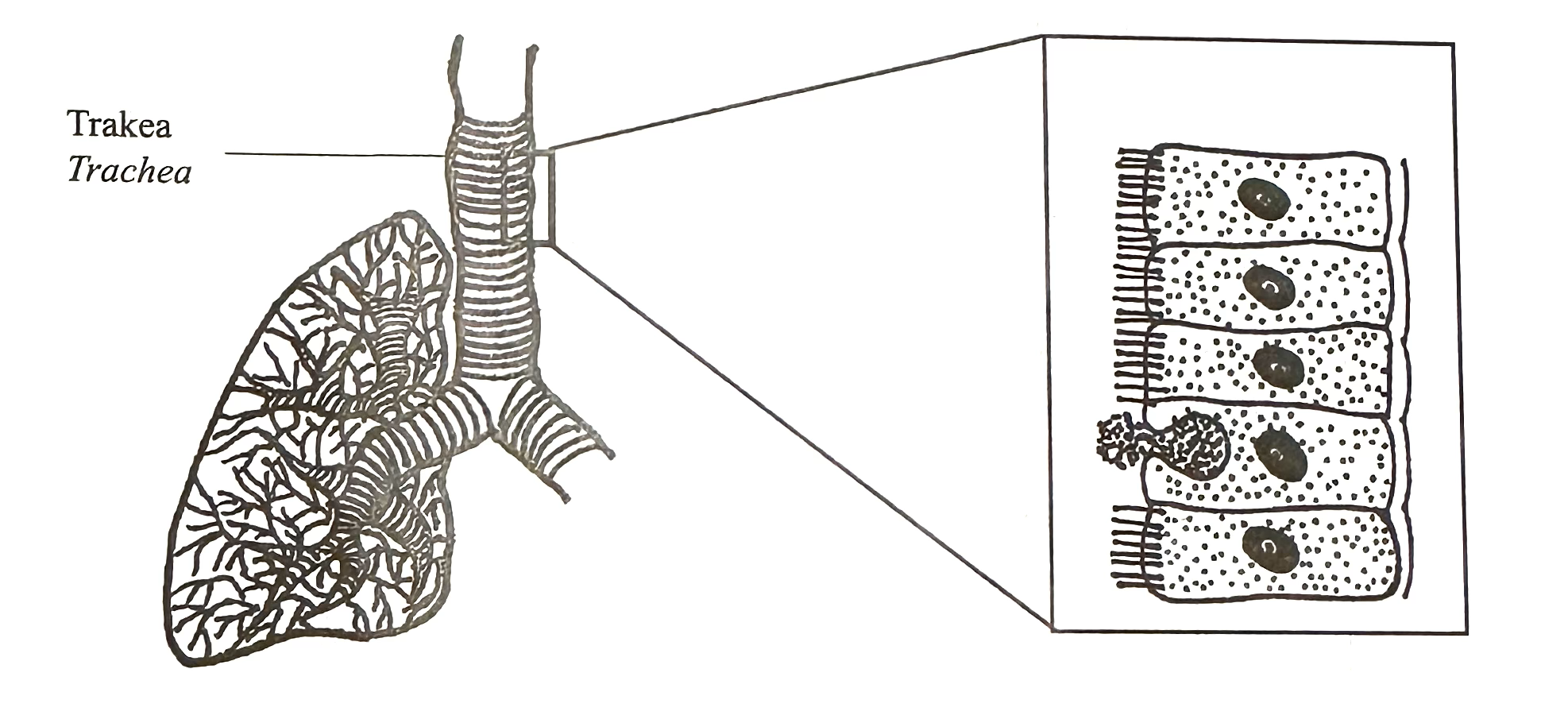
Explain how the membrane lining destroys the bacteria in the air that enters the respiratory system.
[2 marks]
(b) Diagram 9.2 shows a part of the skin of an individual that was pricked with a contaminated needle. After a few days, the part of the wound has pus.
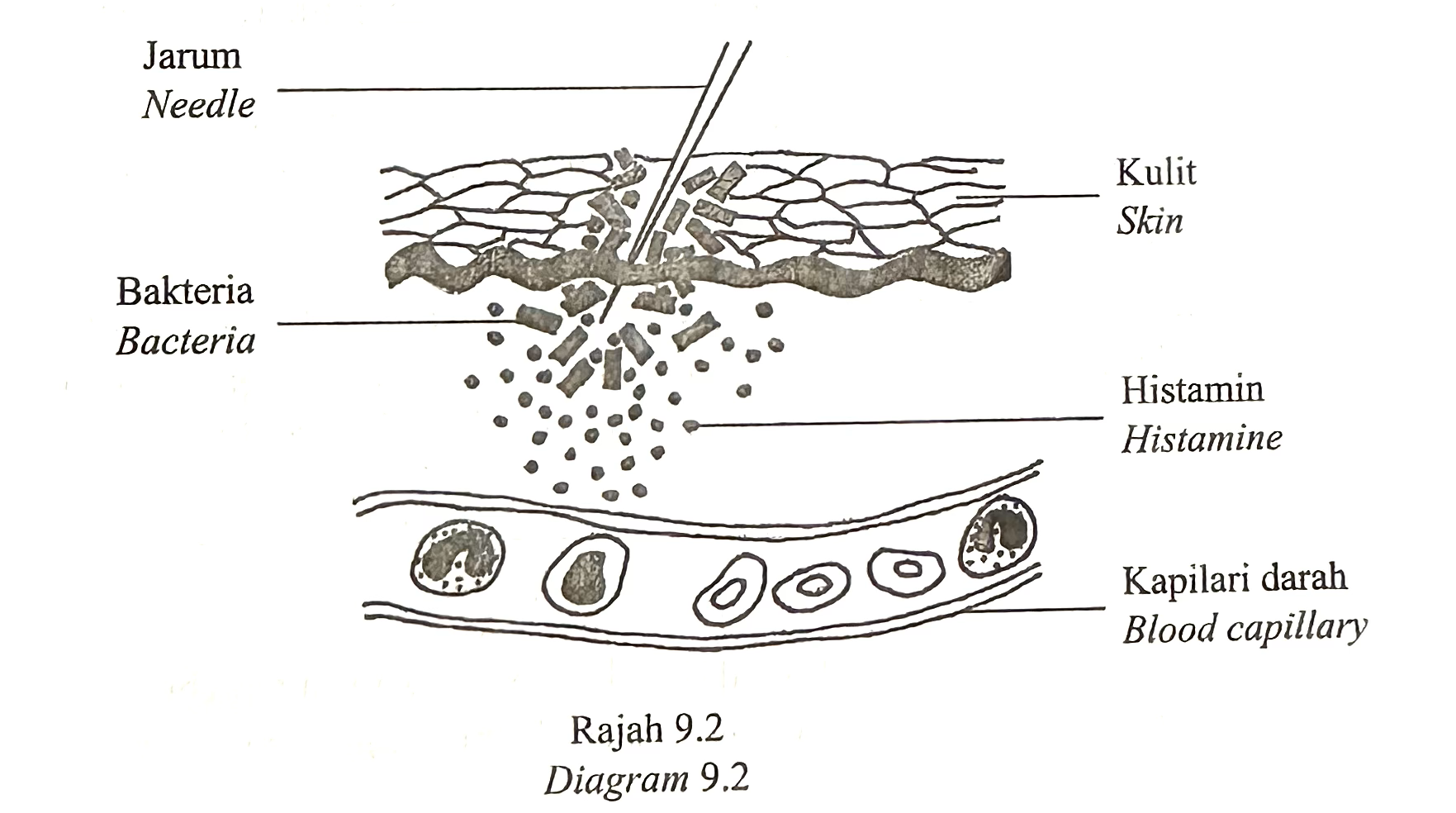
Describe how does the injury stimulate the response of body defence system of the individual to overcome the infection. [8 marks]
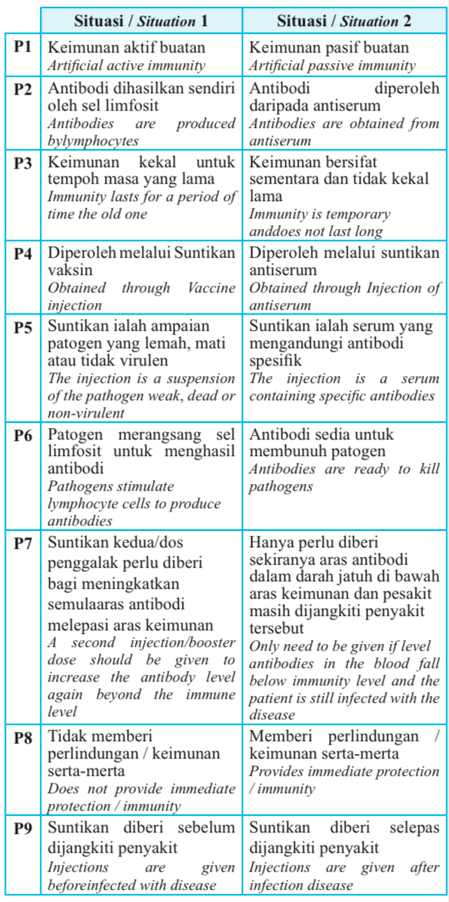
(c) The following information shows two different situations related to immunity in human.
Compare and contrast the types of immunity involved in the two situations.
[10 marks]
Answer:
(a)
1: This layer is a mucous membrane/ secretes mucus// Epithelial cells have cilia
2: Mucus/ cilia trap bacteria// Contain lysozyme
3: Lysozyme decomposes/destroys bacteria
(b)
P: Second line of defense
1: Damaged tissue releases histamine.
2: Histamine stimulates an immediate inflammatory response
3: The inflamed part becomes swollen, red and painful.
4: Histamine causes dilation of blood capillaries
5: to allow more blood flow to the infected area
6: Histamine also increases the permeability of blood capillaries against phagocyte cells
7: The process of phagocytosis occurs
8: To decompose/ destroy bacteria
9: Phagocyte cells / dead tissue form pus
10: Phagocyte cells / clotting factors accumulate in the area of infection
11: The blood clotting mechanism is triggered.
(c)
SET 1 (Artificial active immunity vs. artificial passive immunity) : SIMILARITY
F1: Both involve antibodies
F2: To fight infection
F3: Involves high costs
F4: Materials are injected into the body
F5: Causes allergies/side effects
F6: Involves the interaction between antibodies and antigens
SET 1 (Artificial active immunity vs. artificial passive immunity) : DIFFERENCES
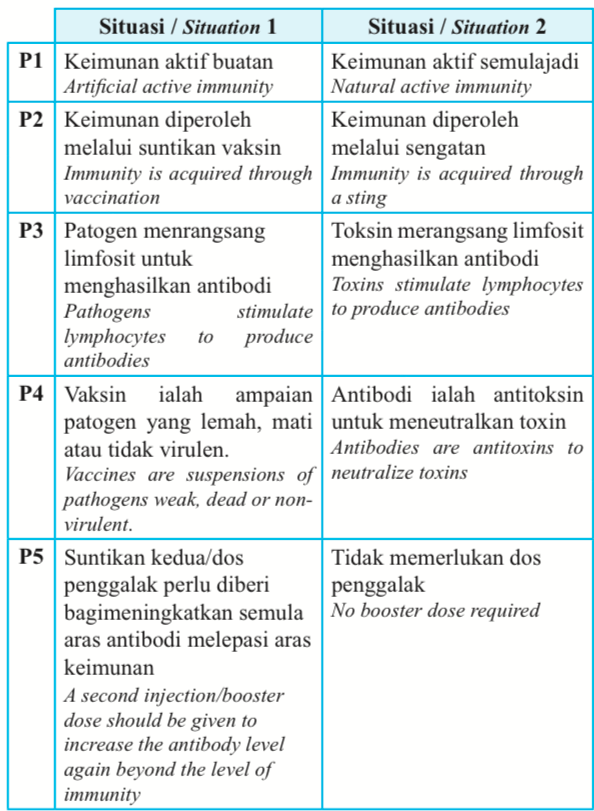
SET 2 (Artificial active immunity vs. natural active immunity, a bee sting stimulates the body to produce antibodies) :
SIMILARITY
F1: Both involve antibodies
F2: To fight infection
F3: Both involve interactions between antibodies and antigens
F4: Both involve the natural production of antibodies by lymphocytes
F5: Both immunities remain for long periods of time
SET 2 (Artificial active immunity vs. natural active immunity, a bee sting stimulates the body to produce antibodies) :
DIFFERENCES
(a) Diagram 9.1 shows a membrane lining that is involved in the human first line of defence.

Explain how the membrane lining destroys the bacteria in the air that enters the respiratory system.
[2 marks]
(b) Diagram 9.2 shows a part of the skin of an individual that was pricked with a contaminated needle. After a few days, the part of the wound has pus.

Describe how does the injury stimulate the response of body defence system of the individual to overcome the infection. [8 marks]
(c) The following information shows two different situations related to immunity in human.
| Situation 1 Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae which causes infections in meningitis and ears. Most of these infections can cause permanent disability and death. According to National Immunisation Schedule, 4-months-old children must be given the first pneumococcal injection to prevent the disease, followed by the second. |
| Situation 2 Insect stings such as wasps commonly cause pain, swelling and redness. During the sting, the venom from the insect flows throughout the victim’s body. This can cause toxic reactions and allergies such as fainting and a drop in blood pressure. An antihistamine injection can be given as a treatment. This antihistamine injection should be given if a person is stung again by this insect. |
[10 marks]
Answer:
(a)
1: This layer is a mucous membrane/ secretes mucus// Epithelial cells have cilia
2: Mucus/ cilia trap bacteria// Contain lysozyme
3: Lysozyme decomposes/destroys bacteria
(b)
P: Second line of defense
1: Damaged tissue releases histamine.
2: Histamine stimulates an immediate inflammatory response
3: The inflamed part becomes swollen, red and painful.
4: Histamine causes dilation of blood capillaries
5: to allow more blood flow to the infected area
6: Histamine also increases the permeability of blood capillaries against phagocyte cells
7: The process of phagocytosis occurs
8: To decompose/ destroy bacteria
9: Phagocyte cells / dead tissue form pus
10: Phagocyte cells / clotting factors accumulate in the area of infection
11: The blood clotting mechanism is triggered.
(c)
SET 1 (Artificial active immunity vs. artificial passive immunity) : SIMILARITY
F1: Both involve antibodies
F2: To fight infection
F3: Involves high costs
F4: Materials are injected into the body
F5: Causes allergies/side effects
F6: Involves the interaction between antibodies and antigens
SET 1 (Artificial active immunity vs. artificial passive immunity) : DIFFERENCES

SET 2 (Artificial active immunity vs. natural active immunity, a bee sting stimulates the body to produce antibodies) :
SIMILARITY
F1: Both involve antibodies
F2: To fight infection
F3: Both involve interactions between antibodies and antigens
F4: Both involve the natural production of antibodies by lymphocytes
F5: Both immunities remain for long periods of time
SET 2 (Artificial active immunity vs. natural active immunity, a bee sting stimulates the body to produce antibodies) :
DIFFERENCES
