Question 10:
(a)(i) Diagram 10.1 shows an activity of an organism.
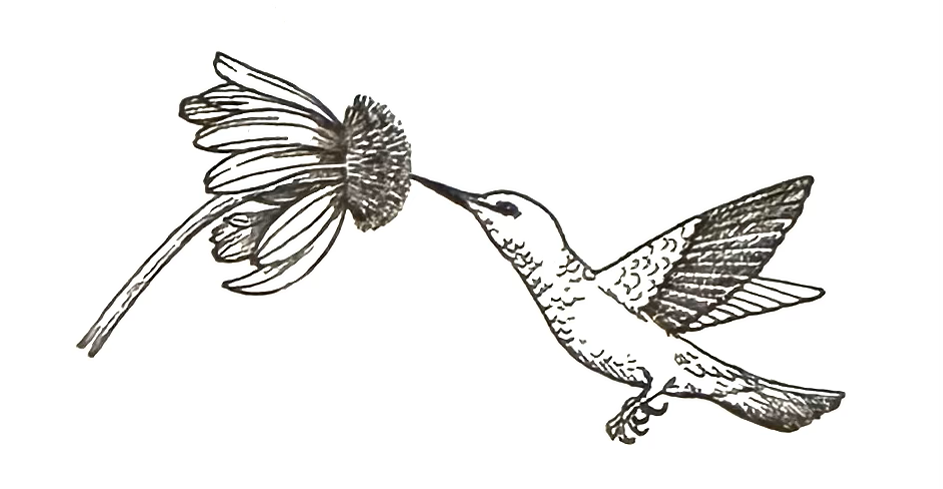

Explain the role of the organism in assisting the transfer of gamete of the flower.
[2 marks]
(ii) Diagram 10.2 shows the development of an embryo in a plant. The zygote divides mitotically to form basal and terminal cells.
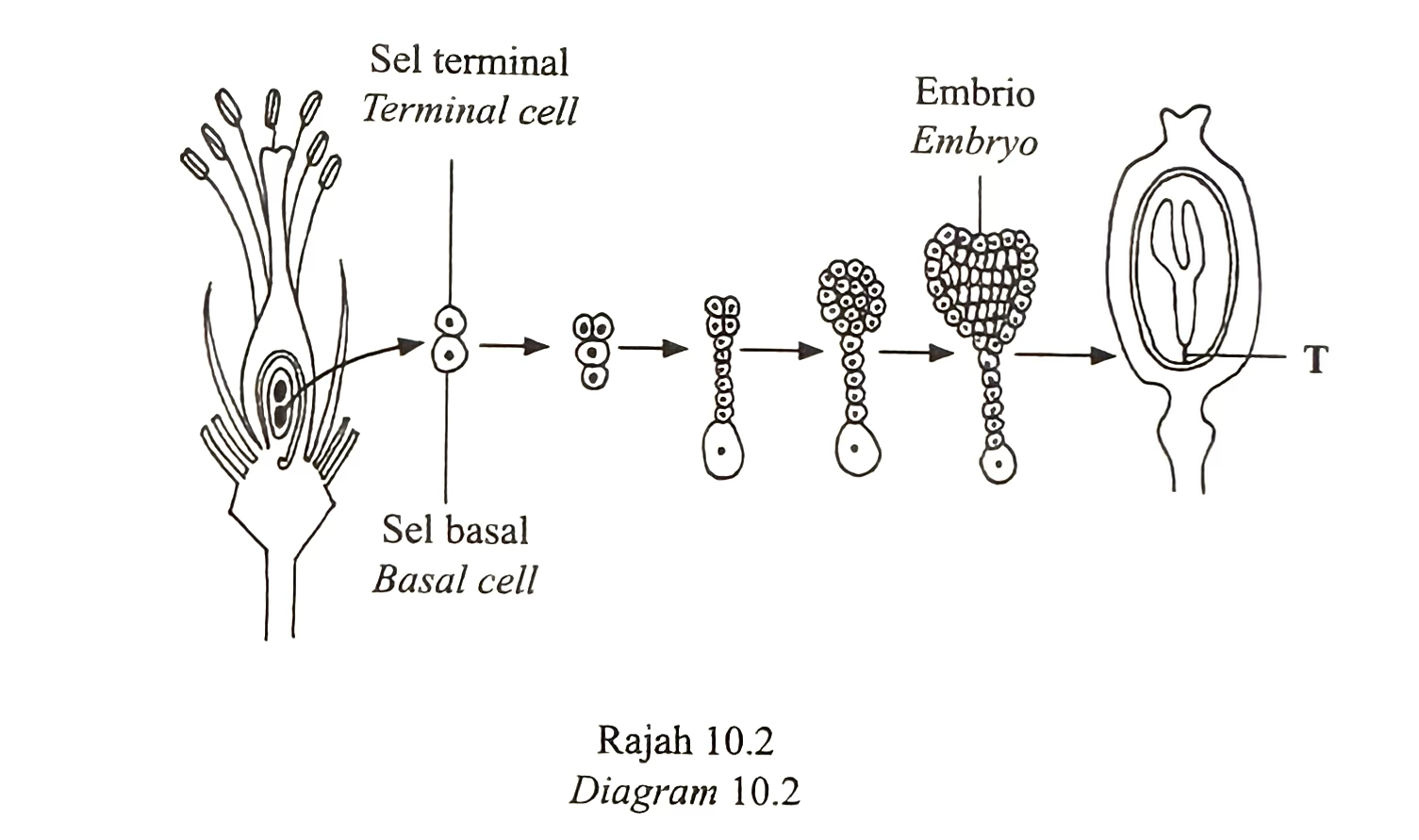
Predict what will happen to the seed development if structure T fails to form. [4 marks]
(iii) Diagram 10.3 shows a longitudinal section of a mango fruit.
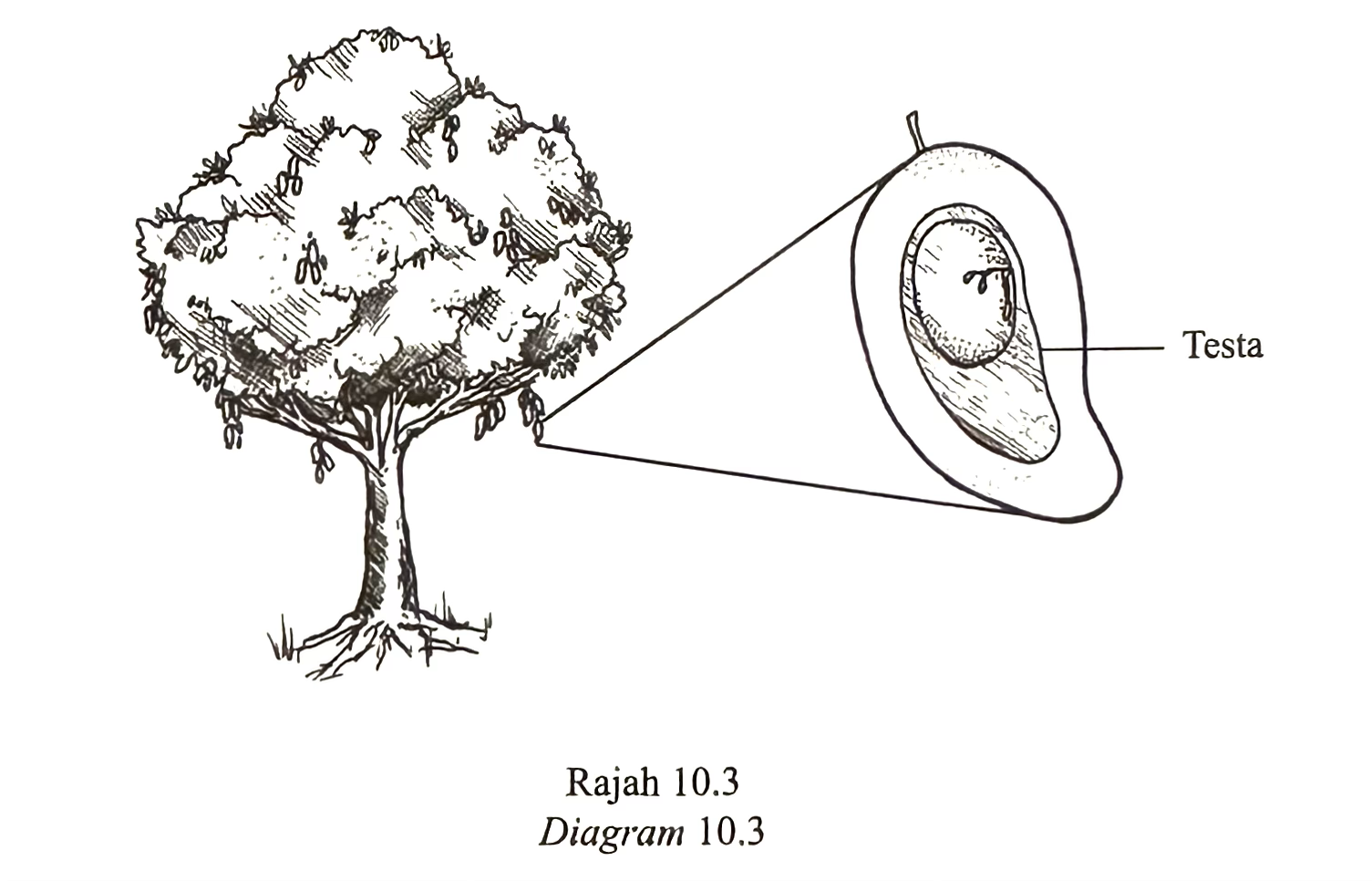
Explain the importance of seeds for the survival of mango plant species. [4 marks]
(b) Diagram 10.4 shows a longitudinal section of a flower. P and Q are the results of a process that happens in structures M and N.
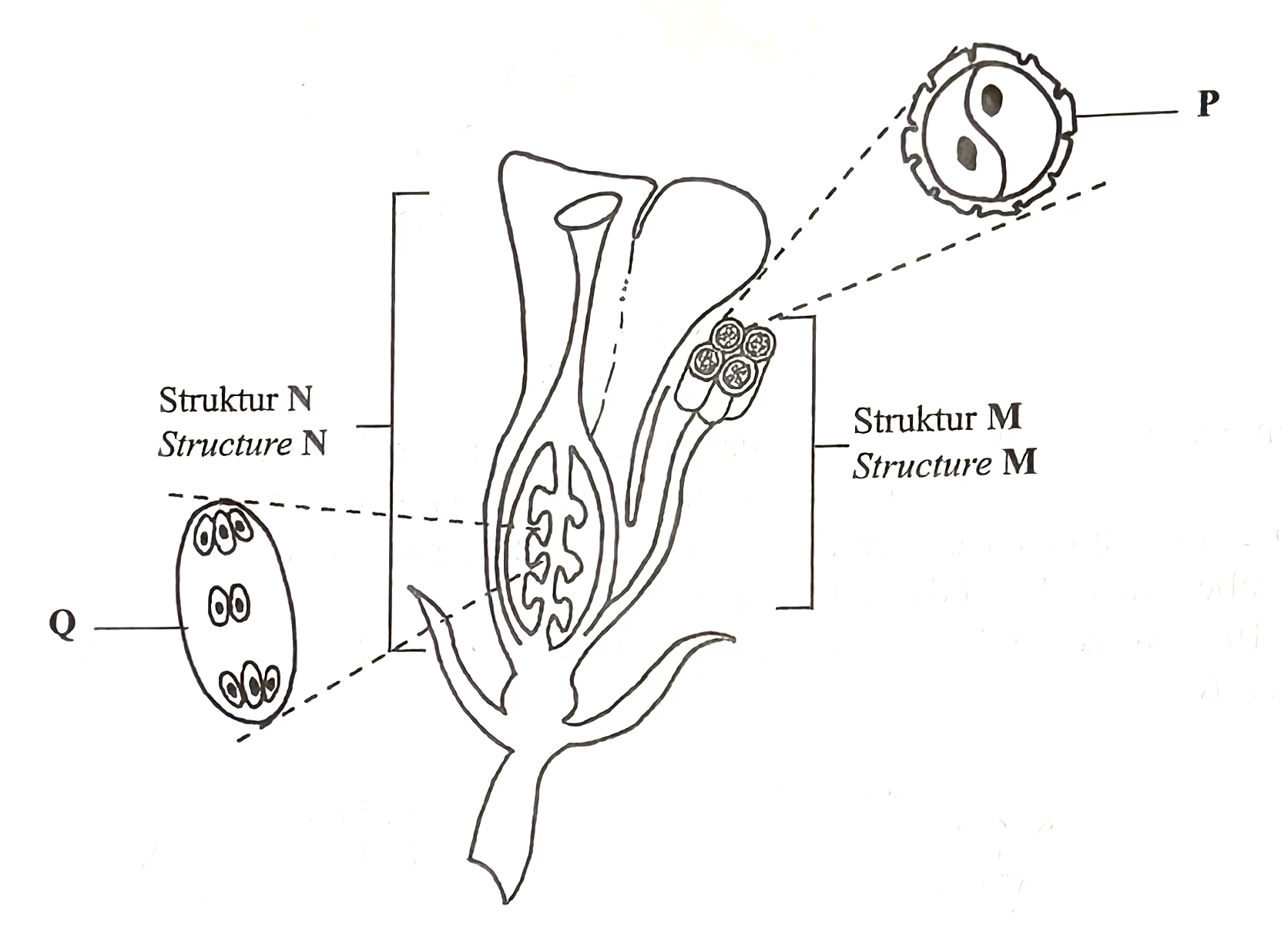
Compare and contrast:
– Structures M and N
– Production processes of P and Q
[10 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
1: Birds are the agents of pollination
2: Transferring pollen/ male gametes// Pollination takes place
3: From anther to stigma
(a)(ii)
1: Small/terminal cells develop into embryos
2: When large/ basal cells do not develop into suspension/ T
3: The embryo cannot be anchored to the wall of the embryo sac// The anchoring of the embryo to the wall of the embryo sac is not formed
4: Nutrients / hormones cannot be supplied to the embryo.
5: The embryo does not develop from the plumule, radicle and cotyledon// Development of the embryo is retarded
6: Seed development is not perfect/defective/stunted
(a)(iii)
1: Seeds have cotyledons / Endosperm tissue
2: Supply nutrients/ energy to the embryo during germination
3: The seed is covered by a strong testa / hard / waterproof// Dormant structure
4: To prevent it from spoiling/ allowing seeds to be stored for a long period of time
5: Seeds contain embryonic structures// to reproduce
6: Germinate to form seedlings// the number of mango trees increases
7: The seeds are covered by spongy tissue/ fruit
8: Easily dispersed/spread to other places
9: Seeds carry genetic information// to adapt
10: Passed down from one generation to another
(b)
SIMILARITIES M and N
F1: Reproductive organs
F2: On the same flower
DIFFERENCE M and N

SIMILARITIES The production process of P and Q
1: Starting with a diploid mother cell // Involved in the production of haploid gametes
2: Involves the process of meiosis
3: Involves the process of mitosis
(a)(i) Diagram 10.1 shows an activity of an organism.

Explain the role of the organism in assisting the transfer of gamete of the flower.
[2 marks]
(ii) Diagram 10.2 shows the development of an embryo in a plant. The zygote divides mitotically to form basal and terminal cells.

Predict what will happen to the seed development if structure T fails to form. [4 marks]
(iii) Diagram 10.3 shows a longitudinal section of a mango fruit.

Explain the importance of seeds for the survival of mango plant species. [4 marks]
(b) Diagram 10.4 shows a longitudinal section of a flower. P and Q are the results of a process that happens in structures M and N.

Compare and contrast:
– Structures M and N
– Production processes of P and Q
[10 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
1: Birds are the agents of pollination
2: Transferring pollen/ male gametes// Pollination takes place
3: From anther to stigma
(a)(ii)
1: Small/terminal cells develop into embryos
2: When large/ basal cells do not develop into suspension/ T
3: The embryo cannot be anchored to the wall of the embryo sac// The anchoring of the embryo to the wall of the embryo sac is not formed
4: Nutrients / hormones cannot be supplied to the embryo.
5: The embryo does not develop from the plumule, radicle and cotyledon// Development of the embryo is retarded
6: Seed development is not perfect/defective/stunted
(a)(iii)
1: Seeds have cotyledons / Endosperm tissue
2: Supply nutrients/ energy to the embryo during germination
3: The seed is covered by a strong testa / hard / waterproof// Dormant structure
4: To prevent it from spoiling/ allowing seeds to be stored for a long period of time
5: Seeds contain embryonic structures// to reproduce
6: Germinate to form seedlings// the number of mango trees increases
7: The seeds are covered by spongy tissue/ fruit
8: Easily dispersed/spread to other places
9: Seeds carry genetic information// to adapt
10: Passed down from one generation to another
(b)
SIMILARITIES M and N
F1: Reproductive organs
F2: On the same flower
DIFFERENCE M and N

SIMILARITIES The production process of P and Q
1: Starting with a diploid mother cell // Involved in the production of haploid gametes
2: Involves the process of meiosis
3: Involves the process of mitosis