- Lipids are complex organic compounds that made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Some lipids contain the elements nitrogen and phosphorus.
- The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in a lipid molecule is higher than the 2 : 1 ratio in carbohydrates.
- Lipids are insoluble in water. However, they are soluble in other lipids and organic solvents such as alcohol and acetone.
- The basic units of lipids are fatty acids and glycerol. A lipid molecule is made up of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid.
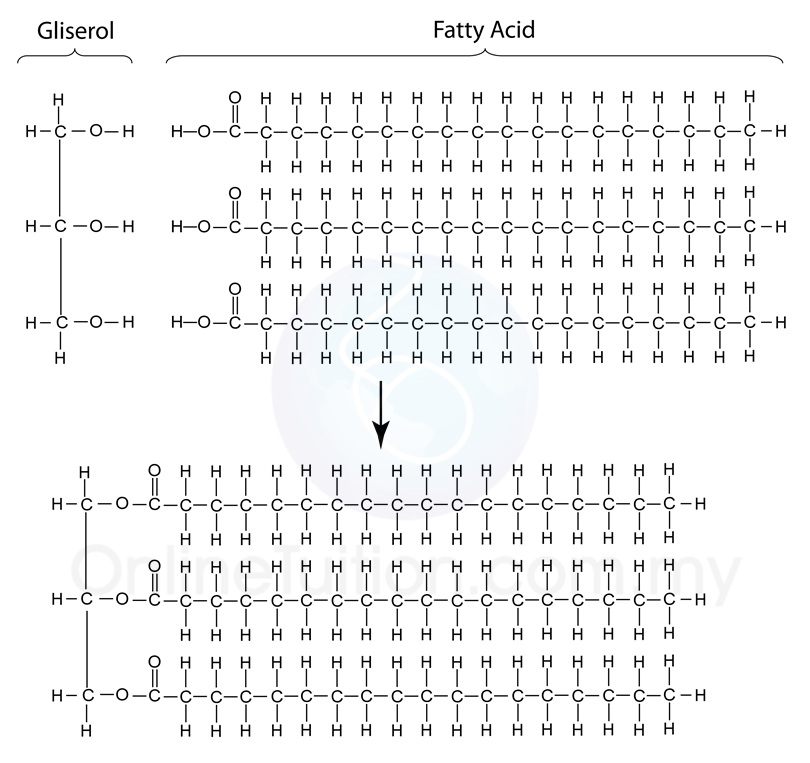
(Formation of molecule of lipid)
Types of Lipids
- Examples of lipids include
- fats and oils (triglycerides),
- waxes,
- phospholipids
- steroids.
- Fats and oils (triglycerides)
- A triglyceride is formed from glycerol and three molecules of fatty acids through condensation.
- Triglycerides can be broken down into fatty acids and glycerol by hydrolysis.
- There are two types of fats.
- Saturated fats
- Fats containing saturated fatty acids
- are solids at room temperature.
- Unsaturated fats
- Fats containing unsaturated fatty acids
- usually Iiquid at room temperature
- it is called oil
- Waxes
- Waxes are long chain esters.
- They are found in the cuticle of leaves.
- They are waterproof
- They can prevents entry of microorganisms and evaporation of water
- Phospholipids
- Phospholipids are component of plasma membrane.
- Example of phospholipid is lecithin. It is a type of triglyceride, which is the main constituent of the plasma membrane.
- Steroids
- Steroids include cholesterol and hormones such as testosterone, oestrogen and progesterone.
- Steroids have a basic structure which consists of four interconnected rings of carbon atoms. Attached to this basic structure are side chains of different lengths.